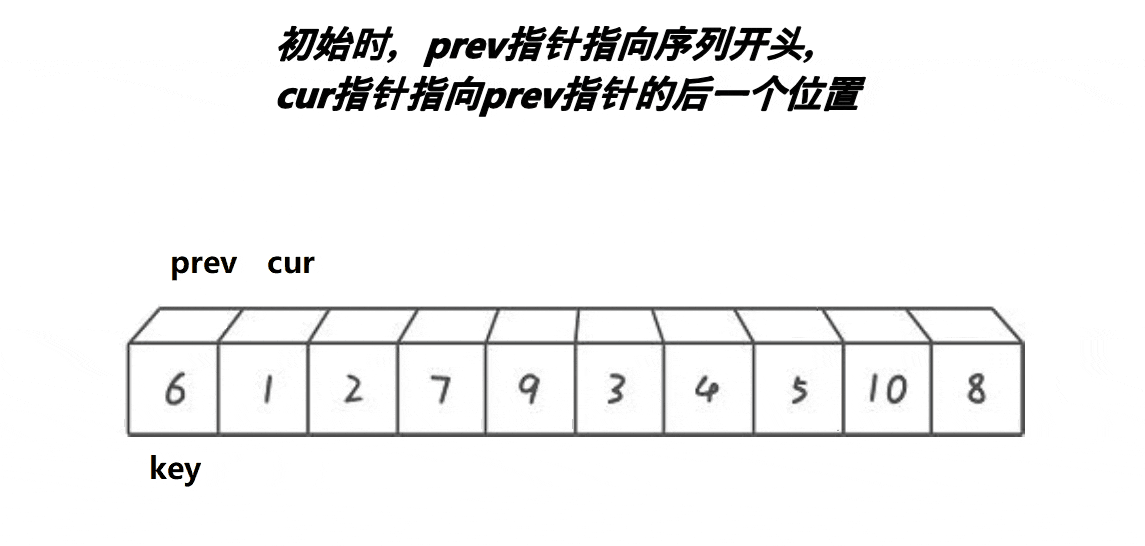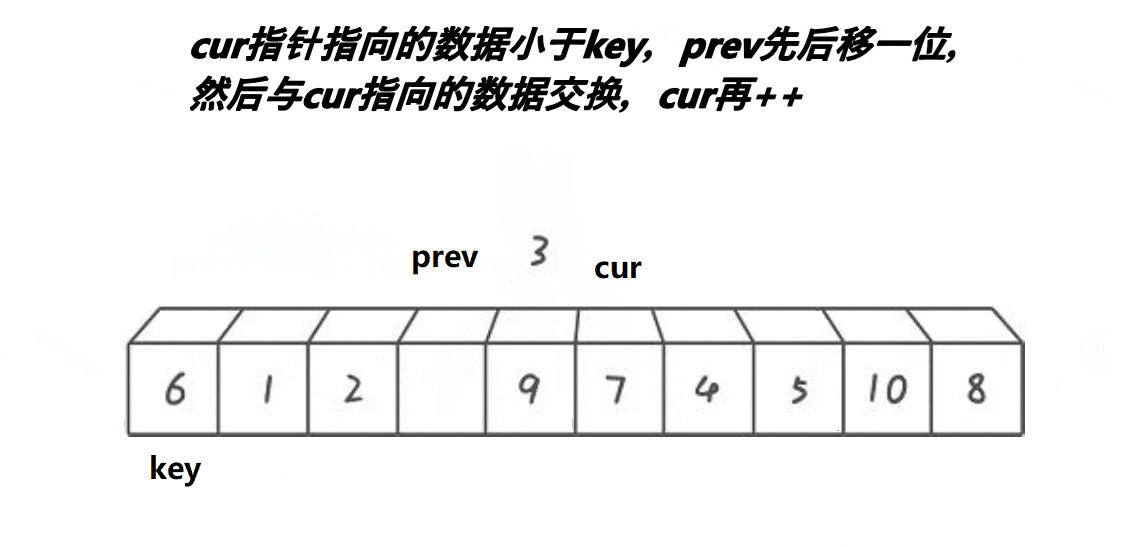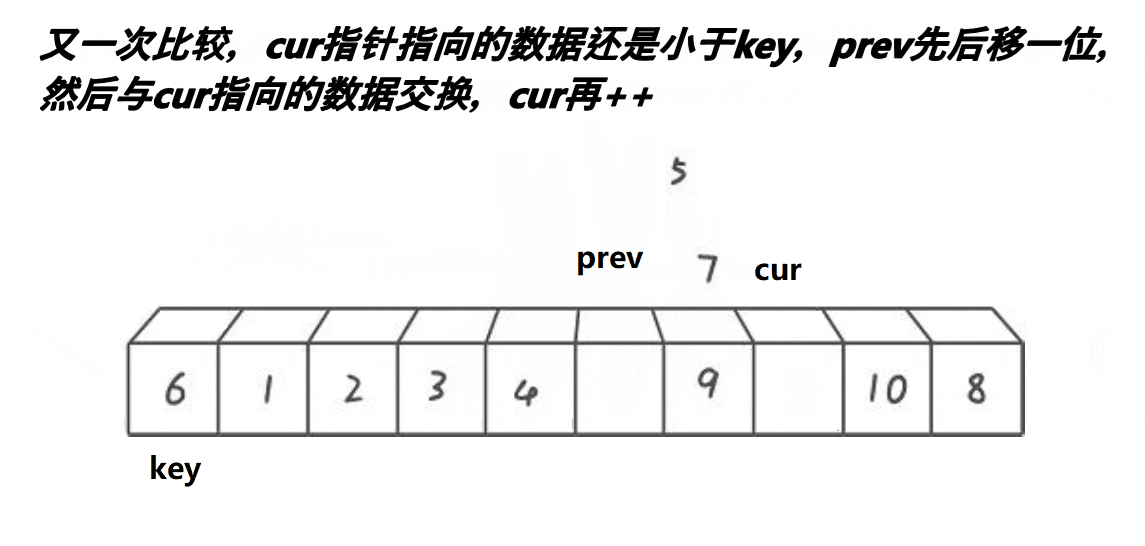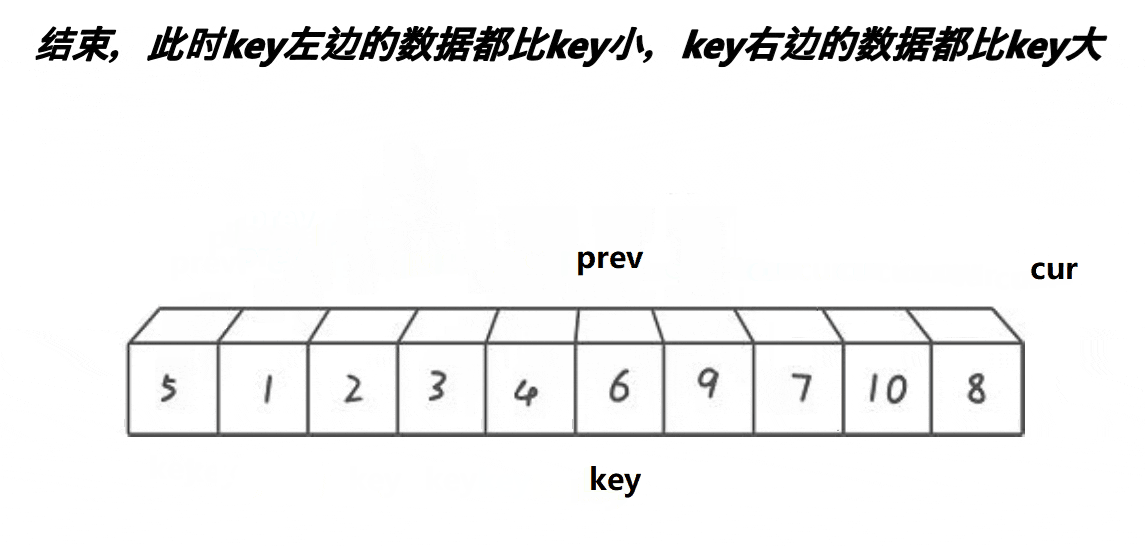
1. yolov8_test.py
import os
import cv2
import numpy as np
from class_type import CLASSES
# 设置对象置信度阈值和非极大值抑制(NMS)阈值。
OBJ_THRESH = 0.25
NMS_THRESH = 0.45
IMG_SIZE = (640, 640)
def filter_boxes(boxes, box_confidences, box_class_probs):
# 筛选出满足条件的框,根据置信度和类别概率筛选出有效的框。
box_confidences = box_confidences.reshape(-1)
# candidate, class_num = box_class_probs.shape
class_max_score = np.max(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
classes = np.argmax(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
_class_pos = np.where(class_max_score * box_confidences >= OBJ_THRESH)
scores = (class_max_score * box_confidences)[_class_pos]
boxes = boxes[_class_pos]
classes = classes[_class_pos]
return boxes, classes, scores
def nms_boxes(boxes, scores):
# 使用非极大值抑制(NMS)来消除冗余框,保留最优的检测框。
x = boxes[:, 0]
y = boxes[:, 1]
w = boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]
h = boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]
areas = w * h
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
xx1 = np.maximum(x[i], x[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y[i], y[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x[i] + w[i], x[order[1:]] + w[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y[i] + h[i], y[order[1:]] + h[order[1:]])
w1 = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 0.00001)
h1 = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 0.00001)
inter = w1 * h1
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
inds = np.where(ovr <= NMS_THRESH)[0]
order = order[inds + 1]
keep = np.array(keep)
return keep
# def dfl(position):
# # 改进模型对目标边界框的回归预测,是一种增强的损失函数
# import torch
# x = torch.tensor(position)
# n, c, h, w = x.shape
# p_num = 4
# mc = c // p_num
# y = x.reshape(n, p_num, mc, h, w)
# y = y.softmax(2)
# acc_metrix = torch.tensor(range(mc)).float().reshape(1, 1, mc, 1, 1)
# y = (y * acc_metrix).sum(2)
# return y.numpy()
#############################################################
### 不需要torch
def dfl(position):
# 用来改进模型对目标边界框的回归预测
# print('111111111111111', position.shape)
n, c, h, w = position.shape
p_num = 4
mc = c // p_num
y = position.reshape(n, p_num, mc, h, w)
y = softmax(y, 2)
acc_metrix = np.arange(mc).reshape(1, 1, mc, 1, 1)
y = (y * acc_metrix).sum(2)
return y
def softmax(data, dim):
max = np.max(data, axis=dim, keepdims=True).repeat(data.shape[dim], axis=dim)
exps = np.exp(data - max)
return exps / np.sum(exps, axis=dim, keepdims=True)
#############################################################
def box_process(position):
# 处理边界框的坐标,将其转换为实际图像上的坐标。
grid_h, grid_w = position.shape[2:4]
col, row = np.meshgrid(np.arange(0, grid_w), np.arange(0, grid_h))
col = col.reshape(1, 1, grid_h, grid_w)
row = row.reshape(1, 1, grid_h, grid_w)
grid = np.concatenate((col, row), axis=1)
stride = np.array([IMG_SIZE[1] // grid_h, IMG_SIZE[0] // grid_w]).reshape(1, 2, 1, 1)
position = dfl(position)
box_xy = grid + 0.5 - position[:, 0:2, :, :]
box_xy2 = grid + 0.5 + position[:, 2:4, :, :]
xyxy = np.concatenate((box_xy * stride, box_xy2 * stride), axis=1)
return xyxy
def yolov8_post_process(input_data):
# 模型输出的原始预测结果经过后处理,以生成最终的检测结果
print(len(input_data))
boxes, scores, classes_conf = [], [], []
default_branch = 3 # 输入数据分成三部分进行处理
pair_per_branch = len(input_data) // default_branch
print("aaaaaaaaaaa",pair_per_branch)
# 处理每个分支数据
for i in range(default_branch):
boxes.append(box_process(input_data[pair_per_branch * i]))
classes_conf.append(input_data[pair_per_branch * i + 1])
scores.append(np.ones_like(input_data[pair_per_branch * i + 1][:, :1, :, :], dtype=np.float32))
# 将输入张量 _in 重新排列并展平
def sp_flatten(_in):
ch = _in.shape[1] # 获取输入的通道数
_in = _in.transpose(0, 2, 3, 1) # 将通道维度移到最后
return _in.reshape(-1, ch) # 将张量展平为二维
# 使用 sp_flatten 函数展平每个分支的 boxes、classes_conf 和 scores
boxes = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in boxes]
classes_conf = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in classes_conf]
scores = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in scores]
# 将每个分支的展平数据连接成一个整体
boxes = np.concatenate(boxes)
scores = np.concatenate(scores)
classes_conf = np.concatenate(classes_conf)
# 过滤框
boxes, classes, scores = filter_boxes(boxes, scores, classes_conf)
# nms--非极大值抑制
nboxes, nclasses, nscores = [], [], []
for c in set(classes):
inds = np.where(classes == c)
b = boxes[inds]
c = classes[inds]
s = scores[inds]
keep = nms_boxes(b, s)
if len(keep) != 0:
nboxes.append(b[keep])
nclasses.append(c[keep])
nscores.append(s[keep])
if not nclasses and not nscores:
return None, None, None
boxes = np.concatenate(nboxes)
classes = np.concatenate(nclasses)
scores = np.concatenate(nscores)
return boxes, classes, scores
def draw(image, boxes, scores, classes):
# 画框
print("{:^12} {:^12} {}".format('class', 'score', 'xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax'))
print('-' * 50)
for box, score, cl in zip(boxes, scores, classes):
top, left, right, bottom = [int(_b) for _b in box]
# print("%s @ (%d %d %d %d) %.3f" % (CLASSES[cl], top, left, right, bottom, score))
cv2.rectangle(image, (top, left), (right, bottom), (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(image, '{0} {1:.2f}'.format(CLASSES[cl], score),
(top, left - 6), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (0,255, 0), 2)
print("{:^12} {:^12.3f} [{:>4}, {:>4}, {:>4}, {:>4}]".format(CLASSES[cl], score, top, left, right, bottom))
return image
2. test.py
import time
import cv2
import numpy as np
from coco_utils import COCO_test_helper
from rknnlite.api import RKNNLite
from yolov8_test import yolov8_post_process,draw
from collections import deque
class Model:
def __init__(self, model_path) -> None:
self.rknn_model = model_path
self.rknn_lite = RKNNLite()
print(f'--> Load {self.rknn_model} model')
ret = self.rknn_lite.load_rknn(self.rknn_model)
if ret != 0:
print('Load RKNNLite model failed')
exit(ret)
print('done')
# 初始化运行环境
print('--> Init runtime environment')
ret = self.rknn_lite.init_runtime(core_mask=RKNNLite.NPU_CORE_0_1_2)
if ret != 0:
print('Init runtime environment failed')
exit(ret)
print('done')
def inference(self, img_src, IMG_SIZE):
if img_src is None:
print('Error: image read failed')
return None
self.co_helper = COCO_test_helper(enable_letter_box=True)
img = self.co_helper.letter_box(im=img_src.copy(), new_shape=(IMG_SIZE[1], IMG_SIZE[0]), pad_color=(0, 0, 0))
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img = np.expand_dims(img, 0)
# print(f'--> Running RKNN model')
outputs = self.rknn_lite.inference(inputs=[img])
return outputs
def release(self):
self.rknn_lite.release()
def recover_real_box(self, boxes):
# 还原框
boxes = self.co_helper.get_real_box(boxes)
return boxes
if __name__ == '__main__':
yolo_model_path = 'yolov8-main/study/yolov8-240617.rknn'
yolo_model = Model(yolo_model_path)
img_path = r"yolov8-main/study/76_269.jpg"
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
yolo_result = yolo_model.inference(img, IMG_SIZE=(640,640))
boxes, classes, scores = yolov8_post_process(yolo_result)
boxes = yolo_model.recover_real_box(boxes=boxes)
after_images = draw(img, boxes, scores, classes)
cv2.imwrite("1.jpg",after_images)
# print(yolo_result)
3. study/class_type.py
CLASSES = ("building", "building2", "statue")
coco_id_list = [1, 2, 3]